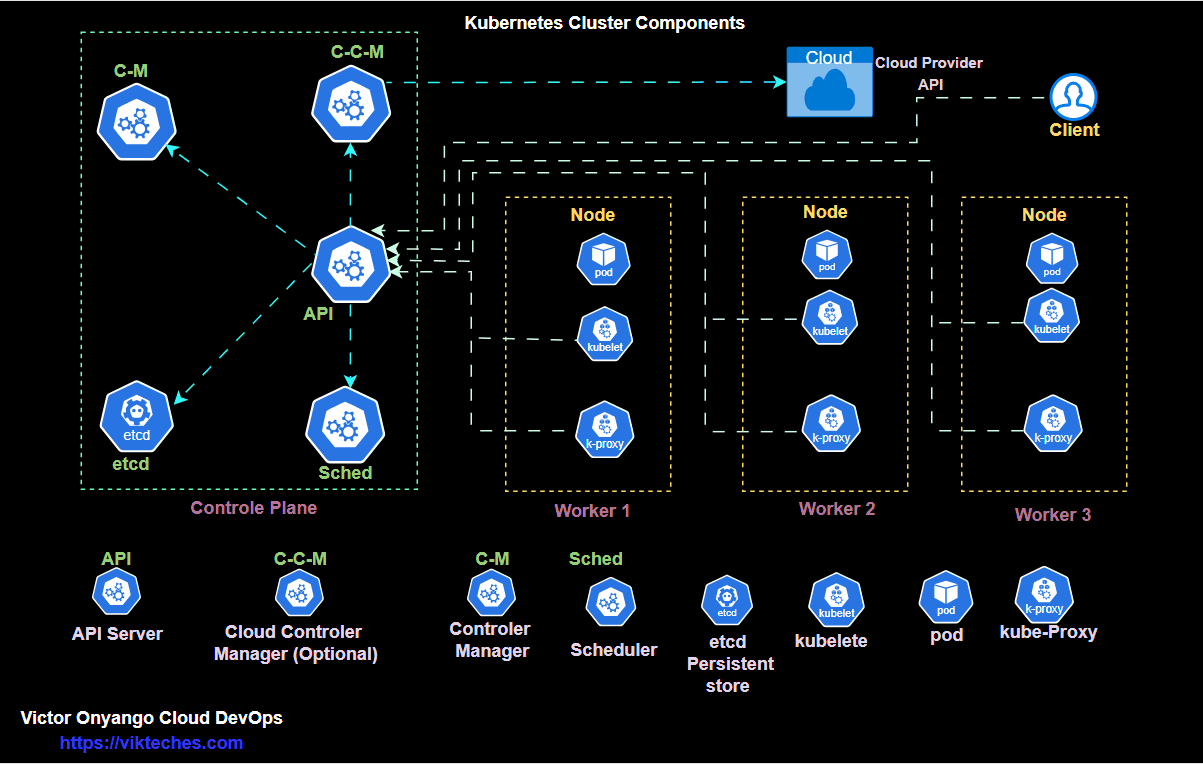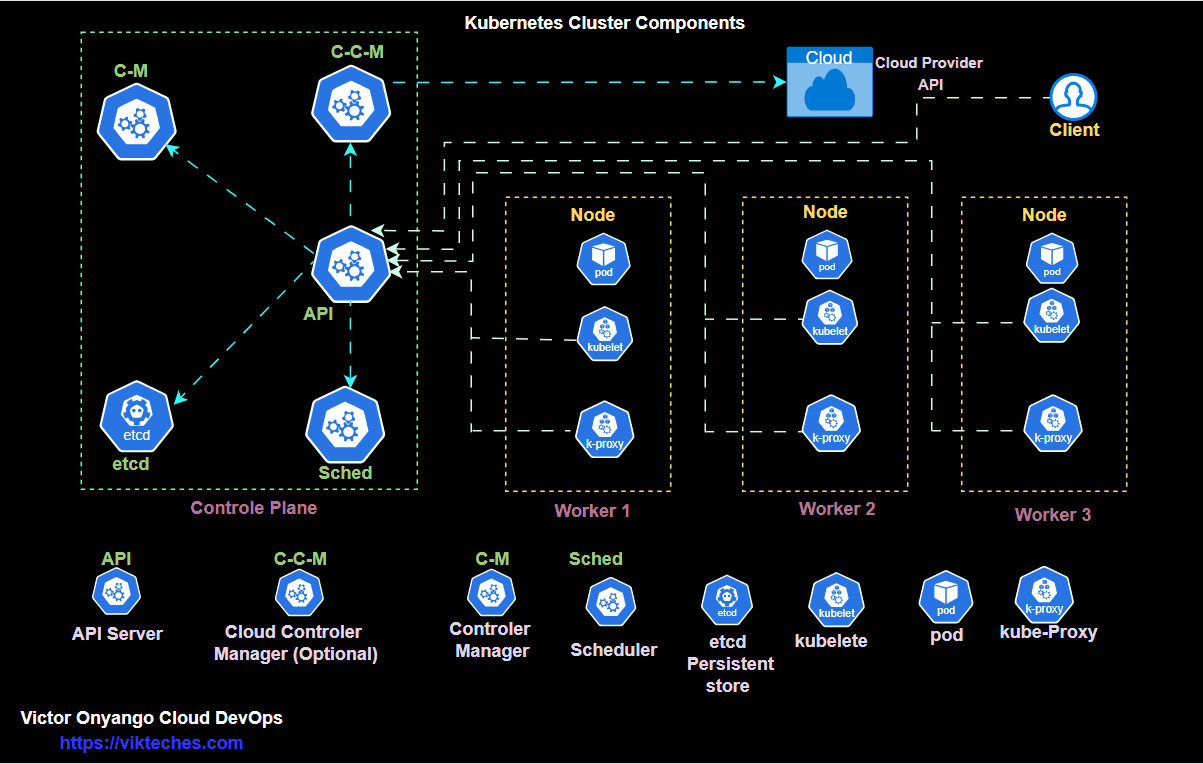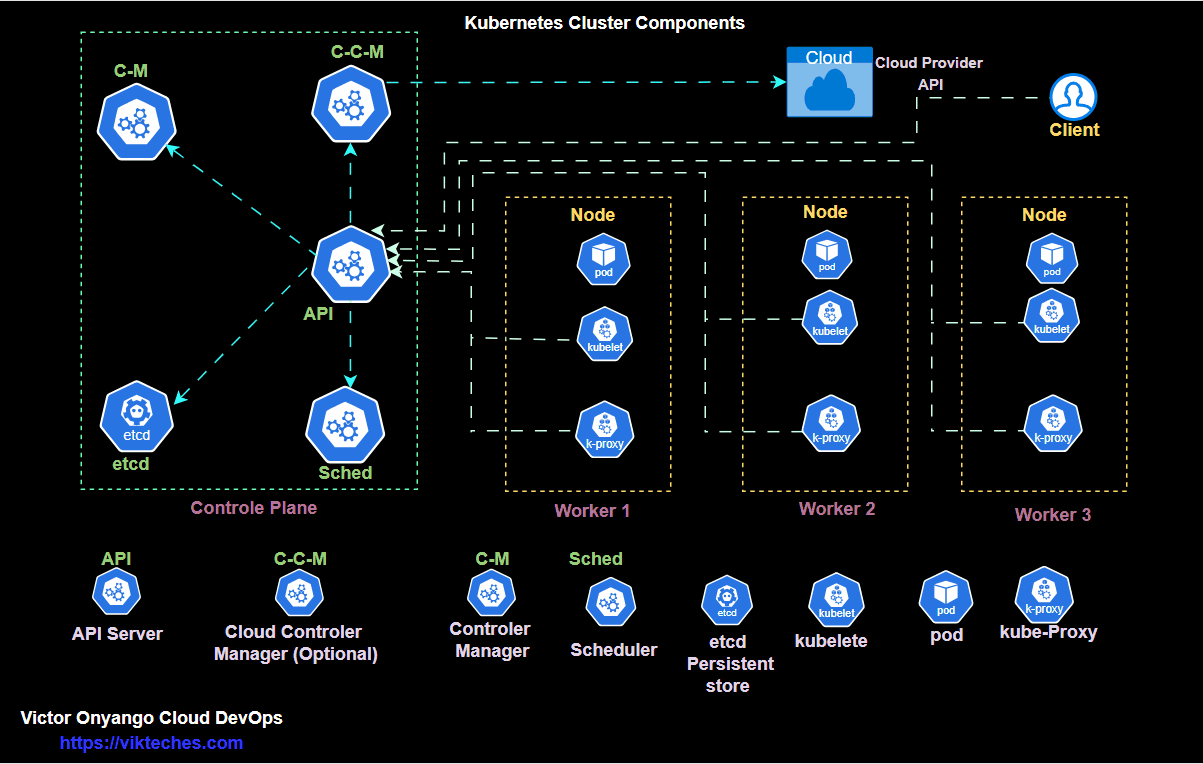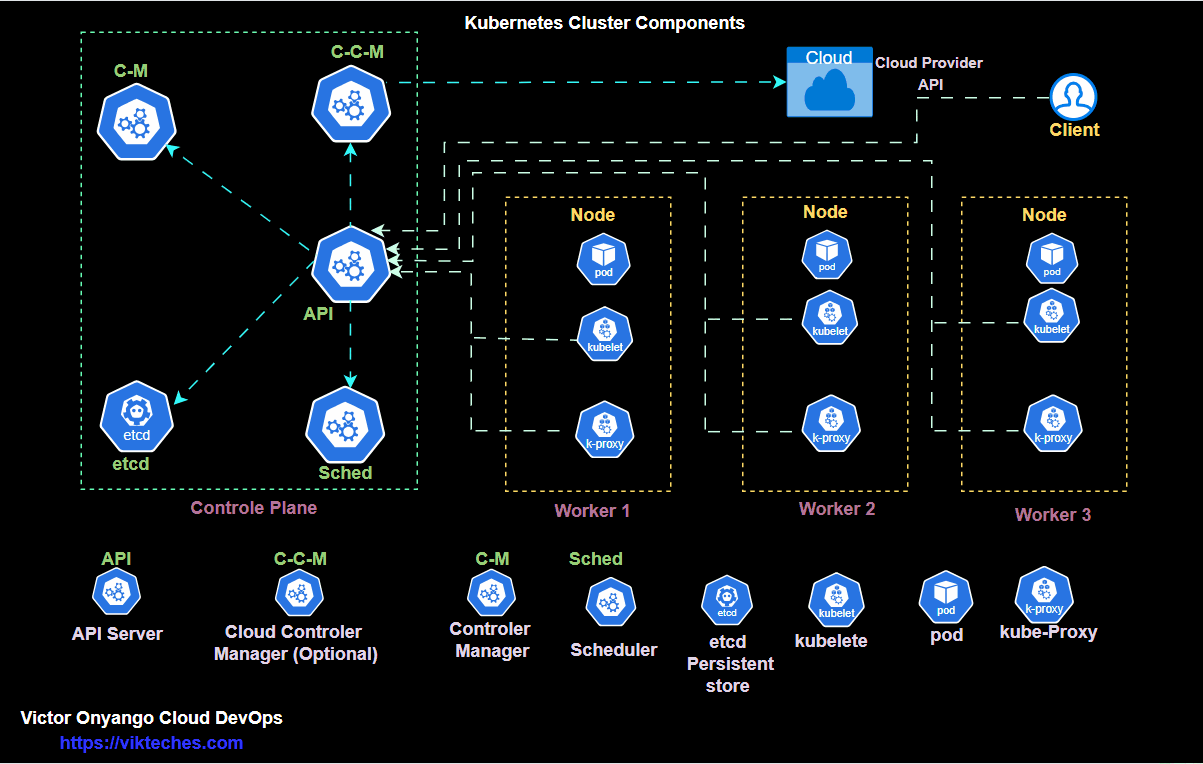
Member-only story
Services — Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, a Service is a method for exposing a network application that is running as one or more Pods in your cluster.
Pod IP are ephemeral in nature.
Pod IP’s are not static they keep changing.
Service ← Theory Part
Advantages
Maintaining a infront of static IP
Load Balancing
Loose Coupling
Kubernetes Service types allow you to specify what kind of Service you want.
ClusterIP — Is accessible only within the cluster
NodePort — Exposes the Service on each Node’s IP at a static port
LoadBalancer — Exposes the Service externally using an external load balancer
Selector → Should match with the pod label ← which pod to be forward?
TargetPort → Is the actual port on which your app is running inside the container ← which port to be forward?
ClusterIP → accessible only within the cluster
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-pod
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx-ctrExecute the pod
kubectl apply -f nginx-pod.yml
kubectl get pods