Member-only story
ReplicaSet — Kubernetes
A Kubernetes Deployment is used to tell Kubernetes how to create or modify instances of the pods that hold a containerized application.
Deployments can scale the number of replica pods, enable the rollout of updated code in a controlled manner, or roll back to an earlier deployment version if necessary.
A ReplicaSet is a process that runs multiple instances of a Pod and keeps the specified number of Pods constant.
ReplicaSet ← Theory Part
Its purpose is to maintain the specified number of Pod instances running in a cluster at any given time to prevent users from losing access to their application when a Pod fails or is inaccessible.
A Replication Controller is a structure that enables you to easily create multiple pods, and then make sure that that number of pods always exists. If a pod does crash, the Replication Controller replaces it.
First, check any pods running on minikube
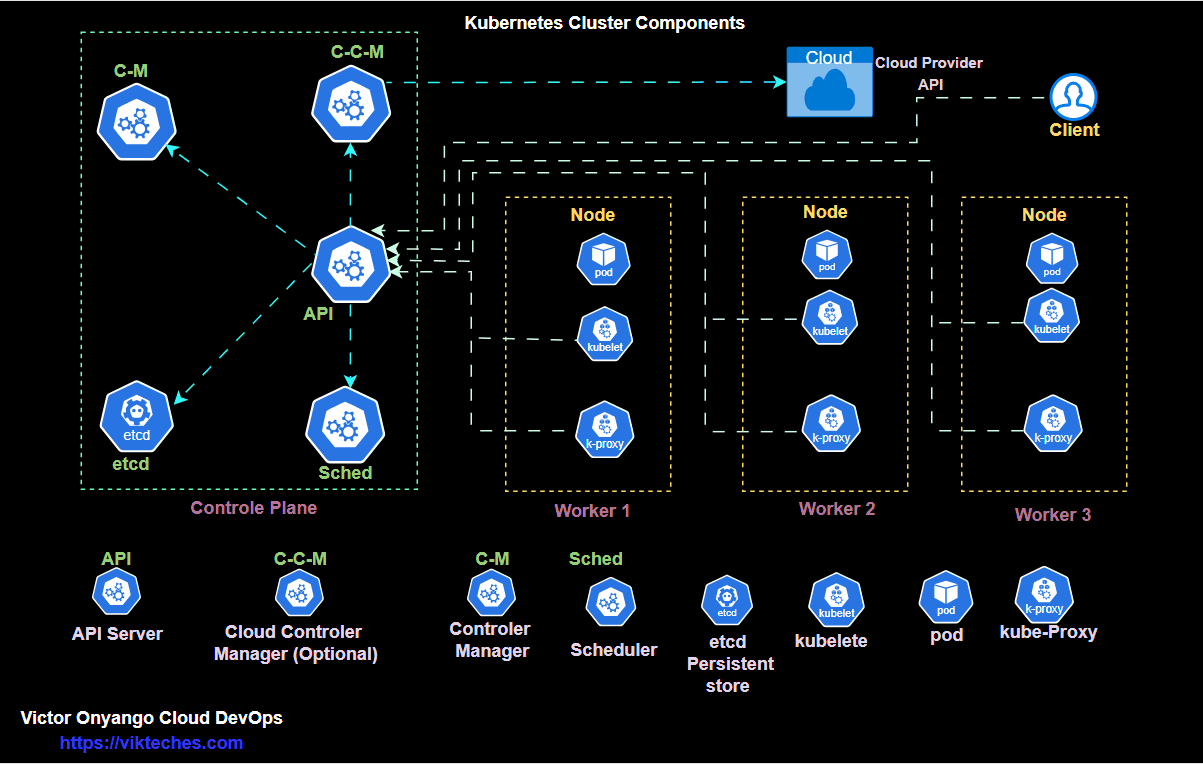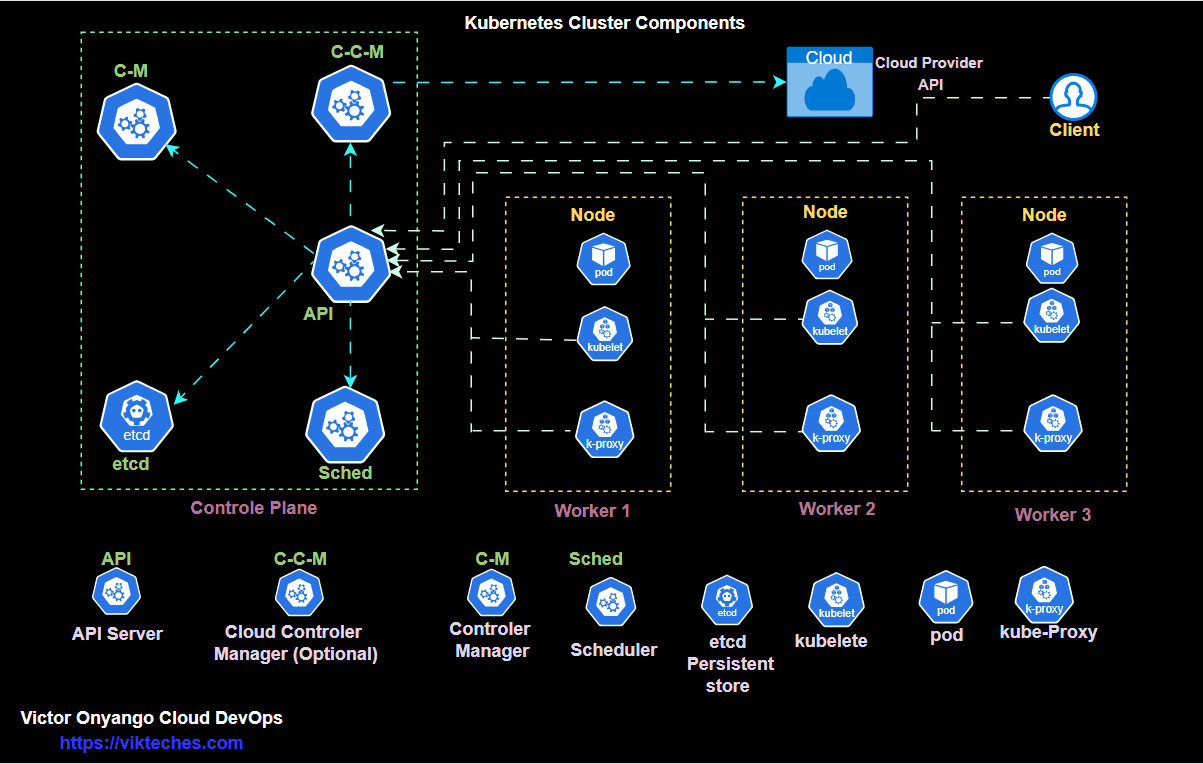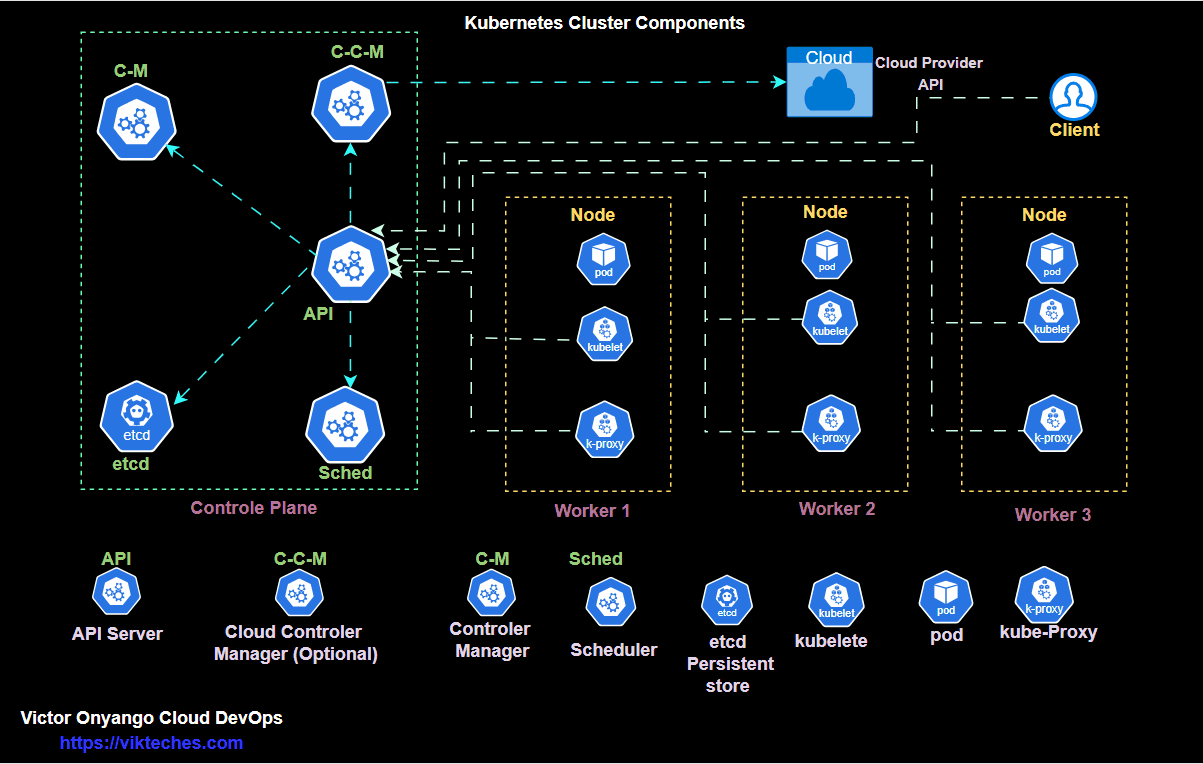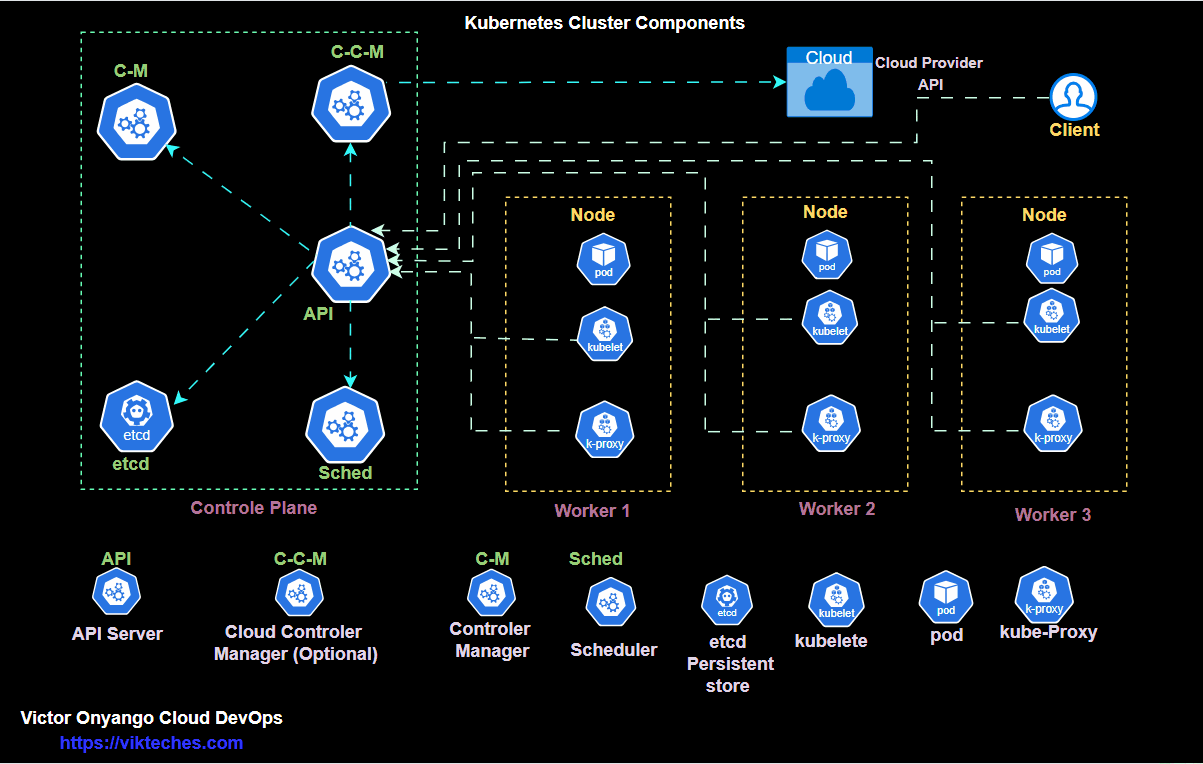
kubectl get podsKubernetes architecture only run
kubectl get all -A
Deploy → ReplicaSet → PodCreate a deployment.yml file